We are proud to announce that the software engineering team from the College of Computer Science and Technology has received Distinguished Paper Awards at both The ACM International Conference on the Foundations of Software Engineering (FSE 2025) and The ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis (ISSTA 2025). These prestigious conferences were held concurrently in Trondheim, Norway.
The award-winning papers are:
"Less is More: On the Importance of Data Quality for Unit Test Generation"
*"LLM4SZZ: Enhancing SZZ Algorithm with Context-Enhanced Assessment on Large Language Models"*
FSE 2025 received 612 submissions from around the world, with 135 papers accepted. ISSTA 2025 received 550 submissions, accepting 107.
Award Highlights
FSE 2025 Award Certificate

ISSTA 2025 Award Certificate

FSE 2025 Award Ceremony
(Third from left: Professor Xia Xin, Qiushi Distinguished Professor at Zhejiang University; Fourth from left: Professor Hu Xing of Zhejiang University)

ISSTA 2025 Award Ceremony
(Second from left: Tang Lingxiao, Zhejiang University student; Third from left: Professor Bao Lingfeng; Fourth from left: Professor Liu Zhongxin)

About the Conferences
The ACM International Conference on the Foundations of Software Engineering (FSE) is a leading academic conference in software engineering, ranked as a Category A conference by the China Computer Federation (CCF). Now in its 33rd year as of 2025, FSE brings together researchers, educators, and industry professionals to share and discuss cutting-edge ideas, innovations, and trends. It is widely regarded as a premier forum that showcases the forefront of software engineering research worldwide. This year’s acceptance rate was 22.06%.
The ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis (ISSTA) is the flagship conference in software testing and analysis, also ranked as a CCF Category A event. With a history of 34 editions as of 2025, ISSTA provides a platform for global researchers and practitioners to exchange ideas and advances in the field. It continues to lead and influence research directions in software testing and analysis, with this year’s acceptance rate at 19.9%.
About the Award-Winning Research
1. "Less is More: On the Importance of Data Quality for Unit Test Generation"
While recent studies have used large language models (LLMs) to automate unit test generation, the role of dataset quality has been overlooked. This paper addresses that gap by examining how noisy data affects LLM-based test generation and introduces CleanTest, a framework for automatically filtering out low-quality data.
The study identifies eight types of noisy data, with classifications validated by domain experts. Using CleanTest, the team analyzed noise distribution in existing datasets and found significant amounts of low-quality data. The results show that cleaning the data not only improves test coverage and defect detection but also reduces model fine-tuning time by an average of 17.5%.
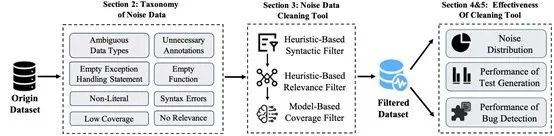
The first author is Zhang Junwei, a fourth-year Ph.D. student, with Associate Professor Hu Xing as the corresponding author. The work is a collaboration between Zhejiang University, Huawei, and Singapore Management University.
Full paper:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3715778
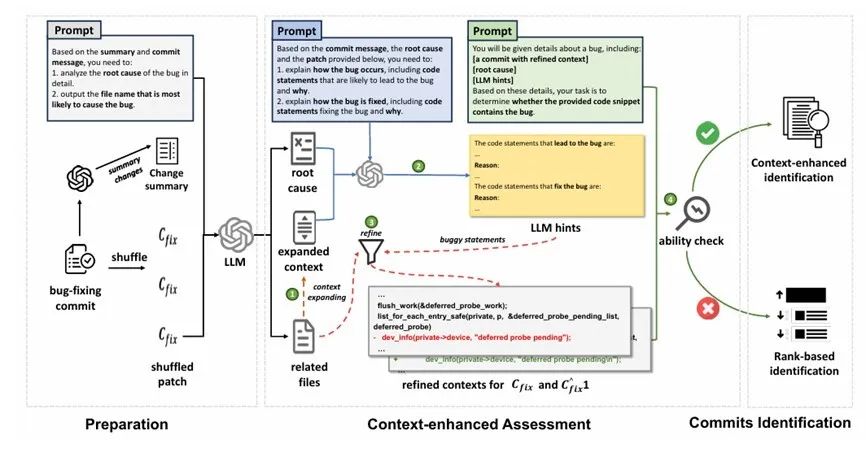
2. "LLM4SZZ: Enhancing SZZ Algorithm with Context-Enhanced Assessment on Large Language Models"
The SZZ algorithm is widely used to identify defect-inducing code commits, but existing versions suffer from limited performance or high complexity. This paper presents LLM4SZZ, a new method that uses large language models to improve accuracy and adaptability.
The approach uses a two-stage strategy: it first assesses whether the LLM can comprehend a specific defect through context-enhanced evaluation. If so, it proceeds with precise identification; otherwise, it switches to a ranking-based method. Tested on three developer-annotated datasets, LLM4SZZ outperformed all baseline methods and successfully identified defects that others missed.
The first author is Tang Lingxiao, a third-year Ph.D. student, and the corresponding author is Associate Professor Bao Lingfeng. Collaborators include Zhejiang University, Hangzhou Binjiang District Blockchain and Data Security Research Institute, and Singapore Management University.
Full paper:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3728885
About the Software Engineering Team
The Software Engineering Team at the College of Computer Science and Technology has established itself as a world-class research group in software analysis, mining, empirical studies, and AI-driven testing. The team consists of talented researchers and developers who have delivered internationally recognized results and built effective partnerships for talent development and industrial innovation. They maintain strong collaborations with institutions such as Singapore Management University, Monash University Australia, and UBC Canada, as well as industry partners including Huawei, State Street Bank, and SPD Bank.