Recently, the State Key Laboratory of Computer Aided Design and Computer Graphics (CAD&CG) at Zhejiang University achieved a major breakthrough at IEEE VIS 2025, a premier international conference in the field of visualization. The lab received oneBest Paper Award and one Best Paper Honorable Mention.
The paper “Causality-Based Visual Analytics of Sentiment Contagion in Social Media Topics”, led by Professor Yingcai Wu’s team, received the conference’s Best Paper Award. This marks the first time a paper with Zhejiang University as the first affiliation has won this honor. The first author of the paper is PhD student Renzhong Li. Focusing on visual analytics of emotion propagation in social media, the work proposes an innovative causality-based method, providing new perspectives and tools for understanding how sentiment spreads across online networks.
In addition, the paper “ConceptViz: A Visual Analytics Approach for Exploring Concepts in Large Language Models”, developed by Professor Wei Chen’s team, was accepted by the conference and received a Best Paper Honorable Mention. The paper is co–first-authored by PhD student Haoxuan Li and student Zhen Wen. Addressing the challenge of interpretability in the internal mechanisms of large language models (LLMs), the authors design an interactive visual analytics framework that integrates an identify–explain–verify workflow. This framework offers a systematic analysis path and validation methodology for exploring how model features map to semantic concepts.
IEEE VIS (IEEE Visualization and Visual Analytics Conference) is a top-tier international conference in visualization and visual analytics, and is listed as a Class-A international academic conference by the China Computer Federation. IEEE VIS covers three core areas—scientific visualization, information visualization, and visual analytics—and is dedicated to advancing cutting-edge research in visualization theories, methods, systems, and applications. Topics include, but are not limited to, large-scale data visualization, immersive analytics, and the integration of artificial intelligence and visualization. Since 1990, the conference has presented a Best Paper Award annually to recognize the most outstanding research in visualization and visual analytics. This year, the conference received 537 paper submissions, of which 131 were accepted. Among these, 5 papers were selected for Best Paper Awards and 12 for Best Paper Honorable Mentions.
Awarded Paper Summaries
Causality-Based Visual Analytics of Sentiment Contagion in Social Media Topics
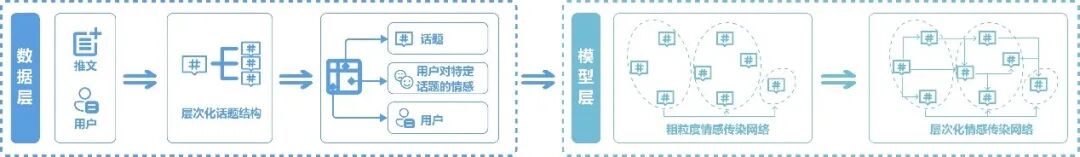
Sentiment contagion network fitting pipeline
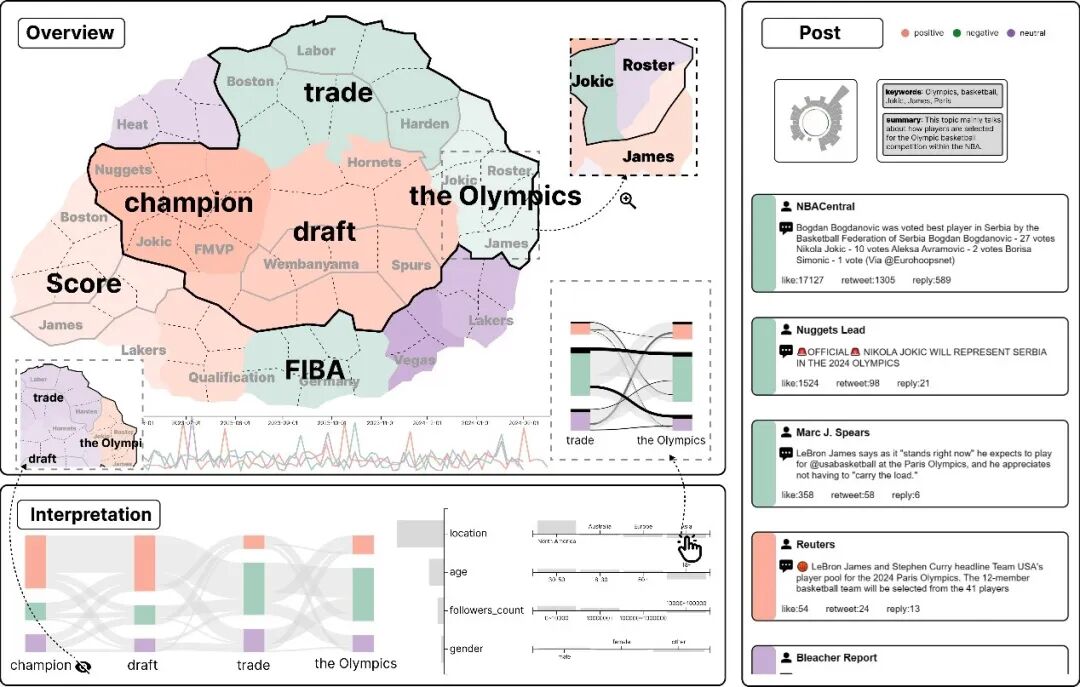
CausalMap system design and main interactions
Sentiment contagion is widespread on social media: a user’s attitude toward one topic can significantly influence their emotional stance on subsequent topics. Analyzing such phenomena involves two key challenges. First, traditional modeling approaches struggle to efficiently construct interpretable, large-scale propagation networks from massive numbers of topics. Second, existing visualization designs fall short in presenting complex sentiment contagion networks and the specific conditions under which contagion occurs, and they are unable to support the visualization of counterfactual impacts of different public opinion guidance strategies within these networks.
To tackle these challenges, this paper introduces a comprehensive causality-driven visual analytics framework. The research team first builds a hierarchical Bayesian network and uses causal discovery algorithms to automatically fit sentiment contagion networks from users’ cross-topic behavioral data. Through the hierarchical design and the incorporation of temporal and topical constraints, the method ensures efficient modeling over large-scale datasets.On this foundation, the paper proposes a novel map-inspired temporal embedding visualization technique. This method encodes the sentiment contagion network as an interactive “contagion map.” The authors further develop CausalMap, a visual analytics system that enables analysts to inspect sentiment transitions and contagion conditions along specific propagation paths, and to explore the potential impacts of various public opinion interventions.A comparative user study demonstrates that, by combining a more effective temporal embedding design with an “explore–explain–intervene” analysis workflow, CausalMap offers powerful support for public opinion monitoring and guidance.
ConceptViz: A Visual Analytics Approach for Exploring Concepts in Large Language Models
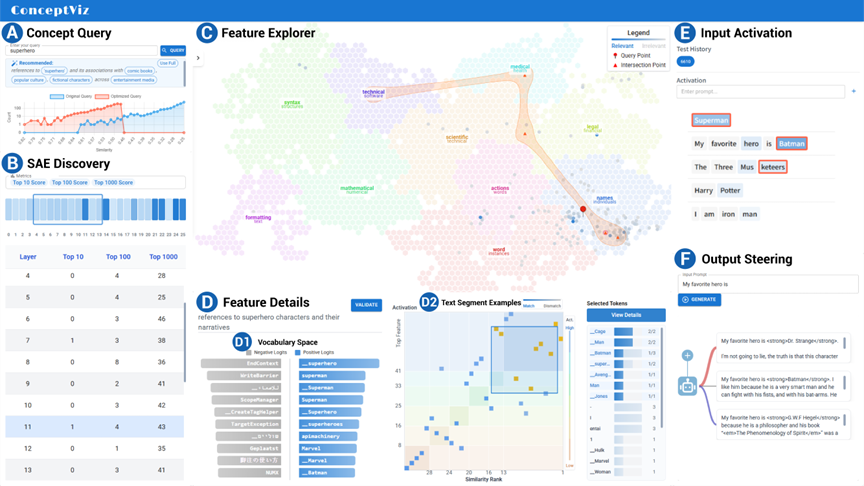
ConceptViz system interface
This paper addresses the major challenge of understanding how knowledge is represented inside large language models (LLMs) and proposes an innovative solution. Sparse autoencoders (SAEs) have emerged as a promising technique for extracting interpretable features from LLMs. However, SAE features cannot be directly aligned with human-understandable concepts, making the interpretation process both labor-intensive and time-consuming.To bridge the gap between SAE features and human concepts, Haoxuan Li and colleagues develop ConceptViz, a visual analytics system that implements a novel “identify ⇒ explain ⇒ verify” analysis pipeline. The system allows users to query the SAE with concepts of interest, interactively explore the alignment between concepts and features, and validate these alignments via model behavior.Through two usage scenarios and a user study, the research team shows that ConceptViz enhances interpretability research by streamlining the discovery and verification of meaningful concept representations in LLMs. Ultimately, it helps researchers form more accurate mental models of LLM features. This work provides important technical support for advancing research on the interpretability, safety, and alignment of large language models.






